As increasing numbers of consumers adopt the little-and-often approach to food shopping, Dan Hunt and Geoff Coleman of Aecom explore the keys to success and typical costs of this competitive sector
01 / INTRODUCTION
The manner in which the UK public approaches food shopping has changed dramatically over the last 10 years. The rise of online ordering and convenience stores mean that the “weekly shop” is no longer a common part of most households’ routine .
Saving time and making food-buying more convenient are the ideals that consumers increasingly demand of our national retailers. It is a challenge that is being met with varying degrees of success in an environment of rising food prices, diminishing disposable income and intense competition for sites. But it is a challenge that has a direct impact on market share, so retailers are taking it very seriously.

02 / CONVENIENCE FOOD SECTOR
Convenience stores that offer about 3,000ft2 of sales area - to meet Sunday trading laws - are generally found in populous and higher-than-average areas of income. They are often in direct competition with each other and will stock a range of goods for either immediate consumption or for consumption within 36 hours of purchase.
It is a format that is proving more and more successful and currently represents about £35bn in sales, or over 20% of the UK food and beverage market, with typical year-on-year growth of 5%. Alongside online sales, this format of store is providing the fastest area of growth for national food retailers as competition intensifies to provide the highest levels of convenience.
The table below shows a broad view of the UK’s leading retailers, the differing levels of maturity of their convenience offer, and a common theme of planned expansion over the next five years:
| Retailer | Current convenience offer | Future plans |
|---|---|---|
| Tesco | About 1,550 Tesco Express stores out of portfolio of 3,100 total stores | Focus of the 830 sites in the pipeline will be on convenience accorrding to chief executive Phil Clarke, with 150 convenience stores opening over the next 12 months |
| Asda | No food-only stores under 3,000ft2 | Converted over 130 former Netto stores to broaden accessibility. Two forecourt trial sites seen by many as a precursor to entry into the convenience market |
| �������Բ����ܰ���’s | More than 500 �������Բ����ܰ���’s Locals in its chain. Has experienced up to 20% year-on-year growth for this format | Actively pursuing new sites for �������Բ����ܰ���’s Locals |
| Morrisons | Opened 12th M Local store in 2013 | Up to 70 convenience stores targeted in the next 12 months. Recently purchased stores from Blockbuster and Jessops in high street locations |
| Co-op | Of its current 3,300 stores, the majority would be considered convenience format | Despite reviews being undertaken over its banking and insurance groups, expansion plans remain in place |
| Marks and Spencer | No Simply Food stores under 3,000ft2; however franchise operations exist in key transport hubs. Over 120 stores opened in partnership with BP in forecourt locations throughout the country. | Targets growth in the Simply Food format with increased numbers of openings planned over the next three years |
| Waitrose | Currently over 30 Little Waitrose stores in its portfolio of about 300 UK stores | Although arguably behind in stated plans of 300 convenience storesby 2018, will continue expansion plans over the next few years |
Most of the UK’s largest food retailers have identified the following as opportunities:
- More readily available sites through increasing high street vacancies as the UK emerges from the recession;
- Continued lifestyle shift to more flexible working, with little-and-often approach to food shopping increasing
- Government plans to relax planning laws, improving opening programmes for proposed stores
- Potential for linking in convenience stores as collection points for orders made at larger stores
- The ability to tailor convenience formats more easily to suit target consumers - for example, a city centre site surrounded by office workers may have a higher proportion of immediate consumption items for lunch hours.
There are large rewards available should these opportunities be captured. The key will be to understand how to do this within the context of the following challenges in the current market:
- Increased competition for prime sites as all food retailers recognise the impact of the convenience market
- This leads to higher rents and more difficult lease negotiations for the retail tenants
- It also leads to “desperation” deals where unsuitable properties with large refurbishment costs are accepted in order to gain access to a market
- Difficulty of pricing as consumers react to rising food prices and lower disposable income
- Understanding the right format for a convenience store;
- Online ordering may become even more convenient than store purchasing if same-day deliveries and increased accessibility to ordering interfaces become a reality.
The next section addresses some of these issues and provides observation on some of the paths taken to date.
03 / KEY ISSUES
Appearance and layout
Many retailers have started to regard the convenience format as a miniature version of their larger format stores. In many instances, this has led to frustration among customers, who seek a full product range in a much smaller selling area. Those that have created a successful look and feel to their stores have made the convenience format something new, distinguishing itself from the larger formats.
A key step for any convenience store retailer is to design the back-of-house space correctly. Convenience store layouts are often characterised by reductions in staff catering space and toilets and a high amount of shared, rather than individual, offices. Those that achieve ratios of more than 70:30 of sales to back-of-house space generally have the more attractive appraisals, despite the associated pain in ripping up the staff facility rulebook in the process.
Location
As with many forms of property investment, location is an incredibly important factor in where to open a convenience store. Seemingly minor details such as which side of the road, an extra 50m to the train station or 5m less frontage can make or break a store.
Units that were previously pubs, banks and even churches have all been successful if they are situated in the perfect location for footfall. The construction cost of combining units or removing asbestos will be dwarfed by the rewards should the location prove to be better than the competition within a particular town or high street. The supply chain should also be thought of when deciding on location: the number of deliveries will increase due to the nature of convenience stock and therefore good access should also be considered.
Competition
The increased competition among retailers for convenience sites can often lead to a paucity of opportunities, as supply by developers or agents has struggled to meet the required national demand. In many locations, this can develop into a rush to land the most lucrative sites, with appraisals being stretched in several directions to secure a prime lease.
The most successful methods of securing schemes focus on speed to site and include the ability to undertake a feasibility survey within 24 hours, a standardised shell specification that breeds familiarity among developers and a reliable cost model that can be adapted to site specifics and fed into any appraisal quickly.
Alliances with agents and developers can create significant pay-offs as potential new developments can be highlighted quickly, with heads of terms signed early to the benefit of all parties. An experienced consultant team will provide invaluable support during this process.
Stock
The key to this question is to make the convenience format flexible. What will fly off the shelves in a busy city centre site may not necessarily work on a residential high street site that may not have associated parking. A modular, almost kit approach to the store layout works, where bolt-ons can be added to suit the customer profile of a particular site.
Consideration should be made to the prepared or fresh food offer of a convenience store - while smaller-scale offers such as baked-in-store produce can work, fully prepared food often skews the appraisal for a particular unit, creating negative returns when the relatively expensive construction costs of these offers are factored in.
One of the main differentiators in the cost of fitting out a convenience store is the percentage of chilled/frozen to ambient goods that are sold. A review of typical layouts from national retailers shows that this can vary by as much as three times the amount of linear or square footage of sales area for chilled goods - which directly impacts the cost of fit-out.
It is not just the additional cost of the chilled units that causes this difference but also the knock-on costs of larger chilled storage facilities, associated plant costs, enhanced mechanical solutions to service the store environment and additional fees to resolve any planning or acoustic issues with the plant required.
Successful layouts have developed a servicing solution to these units that does not require large areas of chilled storage. It is rare that a scissor lift or dock leveller solution can be accommodated within the confined space of a typical convenience store, and therefore tailgate deliveries out of hours and often with goods heading straight to shelf rather than storage becomes the norm.
Procurement and construction
There has been a clear trend among leading retailers in terms of how procurement strategies have changed as their offer and delivery structure have matured. Early attempts took tried and tested consultants from the larger store formats, which then developed a detailed design to pass on to a framework main contractor.
As convenience store programmes have developed, however, consultant roles are being amalgamated and reduced, the main contractor is undertaking more management and design and bureaucracy is being reduced for key decision points.
The final stage, as retailers become confident with their format, is to enter a quasi construction management approach, with large amounts of directly purchased items. A chosen client representative remains from the original consultant list and the main contractor role is often removed as key subcontract packages are procured directly.
There is nothing necessarily wrong with this evolution in approach - the interesting point is the scramble by the consultant and contractor base to retain an involvement in a rapidly decreasing delivery team, as the rewards can still be considerable should they make it.

04 / COST CONSIDERATIONS
As with all projects the location, layout and regional trends have an impact on the outturn construction cost. Competitively tendering, bulk purchasing, securing multi scheme discounts help to achieve value for money. Streamlining the consultant team by using standard store design guides and specifications also helps to reduce capital spend.
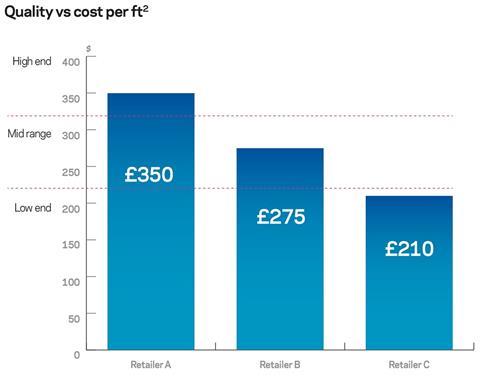
The balance between maintaining a recognisable brand identity but still using a reduced fit-out specification will inevitably have an impact on the overall cost of delivering a convenience store format. The top graph to the right shows how that balance can affect the outturn cost.
As mentioned previously, the level of quality of a convenience store fit-out is partly attributable to the type of food on offer. If there are more ready meals or dairy products, for example, this would require more chilled cabinets, and more M&E associated works will be required to support the offer.
The planned life of the fit-out would be another factor. The quality of the materials used would affect the expected shelf life of the design and materials used. This would typically be dictated by the investment plans of the client, quite possibly in alignment with their expansion plans.
Finally, the type of environment and space that the retailer feels it must provide for their customers can determine final fit-out cost. This could mean higher levels of comfort cooling, or a better quality finish to the sales floor.
In many instances, the customers probably don’t even notice the detailing that would typically attract more costs - for example, providing recessed entrance mats rather than lay-on alternatives.
Needless to say, the ideal solution is to maintain the same level of brand impact as the larger retail outlets, but delivered at a much lower cost. In order for the client to do this, it needs to look at what the key cost drivers are and to find design-friendly solutions to reduce cost in these areas as much as possible.
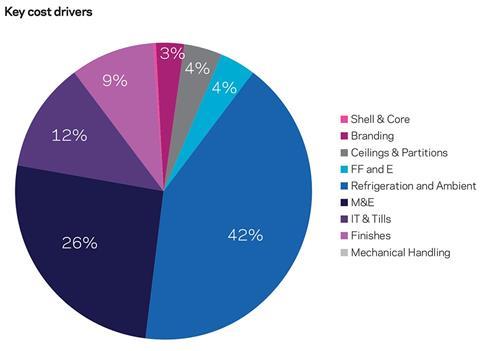
Typically, we’ve found that M&E and refrigeration tend to account for the highest percentage of cost within a convenience scheme. The chart on the right shows that M&E can make up almost 26% of the total construction cost, and refrigeration 42% .
One way of overcoming this could be to install doors on the refrigeration cabinets. This would reduce the level of the M&E design needed to maintain ambient air treatment to the sales floor, and in addition reduce the energy needed to maintain cool air in the refrigeration units.
05 / COST MODEL
The elemental cost model in this article is to create 3,000ft2 net sales floor area on a ground floor. This is a single-storey unit with the back-of-house area located at the rear of the store. The fit-out is within an existing shell, which is owned by the landlord.
The convenience store is of a mid to low range specification, located on a high street in the West Midlands. It has one customer entrance leading onto the high street, with good access at the rear for deliveries.
The construction programme is three weeks. The scheme was competitively tendered using a single-stage design-and-build procurement route. It excludes professional fees, acquisition fees and abnormals, as these are site dependent.
| £ | £/�ڳ�2 NSFA | % of total cost | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Builders’ work to the shell and core | 4,000 | 1.33 | 0.5% |
| Preparation of floor slab, service penetrations @ item £4,000 | |||
| External signage | 11,000 | 3.67 | 1.3% |
| Part illuminated signage @ item £8,500 | |||
| Bus stop projected sign @ item £1,000 | |||
| Temporary window graphics @ item £1,500 | |||
| Ceilings and partitions | 29,000 | 9.67 | 3.5% |
| Tiled ceiling to staff areas 66m2 @ £28 | |||
| Plasterboard ceiling on MF system 85m2 @ £18 | |||
| Bulkheads @ item £3,500 | |||
| Sales floor boxing out @ item £5,250 | |||
| Plasterboard column casing @ item £6,476 | |||
| Plasterboard partitions to form staff areas 58m @ £67 | |||
| 1 hr plasterboard fire rated partitions 13m @ £270 | |||
| Forming holes @ item £3,000 | |||
| Electrical | 93,000 | 31.00 | 11.3% |
| Main supply distribution @ item £11,500 | |||
| Sales floor and back of house lighting @ item £39,500 | |||
| Small power @ item £11,200 | |||
| Containment @ £9,500 | |||
| Cold room detection @ item £11,100 | |||
| Security @ item £10,200 | |||
| Mechanical | 90,000 | 30.00 | 10.9% |
| Gas service supply @ item £1,500 | |||
| Installation of boiler, booster set, pumps, valves, water tank, associated pipe work @ item £16,700 | |||
| Above ground drainage @ item £4,000 | |||
| Hot and cold water services £21,500 | |||
| Sanitary ware @ item £3,000 | |||
| BMS controls @ item £11,000 | |||
| Air conditioning @ item £32,300 | |||
| IT installation | 83,000 | 27.67 | 10.1% |
| Installation of tills, computer network, | |||
| Telecoms @ item £83,000 | |||
| Mechanical handling | 0 | 0 | 0% |
| Not applicable | |||
| Floor finishes | 33,000 | 11.00 | 4.0% |
| Vinyl to sales floor area 279m2 @ £14 | |||
| Anti slip paint to stock room floors 51m2 @ £25 | |||
| Vinyl to staff areas 62m2 @ £17 | |||
| Vinyl to staff WCs 38m2 @ £14 | |||
| Levelling compound and screed @ item £6,000 | |||
| Recessed entrance matt @ item £8,678 | |||
| Skirting’s, edgings and trims @ item £11,555 | |||
| Joinery | 20,000 | 6.67 | 2.4% |
| Internal laminate doors on hardwood frame including ironmongery 2nr @ £816 | |||
| Internal painted timber doors including ironmongery 13 @ £564 | |||
| Boxing out services generally @ item £5,000 | |||
| General fixtures and fittings @ item £6,000 | |||
| Decorations | 6,000 | 2.00 | 0.7% |
| Paint to walls in mist coat and two coats matt 1,345m2 @ £4 | |||
| Paint to doors 13nr @ £45 | |||
| Protection | 3,000 | 1.00 | 0.4% |
| Galvanised posts, Kee Klamp, checker plates and corner angle @ item £3,000 | |||
| Shop fitting | 2,000 | 0.67 | 0.2% |
| Footfall counter @ item £2,000 | |||
| Internal signage | 9,000 | 3.00 | 1.1% |
| Back-of-house signage @ item £1,500 | |||
| Feature signage @ item £5,500 | |||
| Sales floor navigational signage @ item £2,000 | |||
| Refrigeration | 243,000 | 81.00 | 29.5% |
| Loose produce, chilled and frozen display cases @ item £193,000 | |||
| Cold Room @ item £32,000 | |||
| Alarms & monitoring @ item £18,000 | |||
| Ambient | 55,000 | 18.33 | 6.7% |
| Shelving item @ item £33,500 | |||
| Events tables for wine and produce @ item £9,000 | |||
| Bakery shelving and racking @ item £7,500 | |||
| Flowers and plant displays @ item 5,000 | |||
| Till podiums | 5,000 | 1.67 | 0.6% |
| Till housing@ item £5,000 | |||
| Backstage works | 28,000 | 9.33 | 3.4% |
| Racking @ item £9,000 | |||
| Office & canteen equipment @ item £19,000 | |||
| Preliminaries | 111,000 | 37.00 | 13.5% |
| Site set-up @ item £51,000 | |||
| Overheads and profit @ £26,000 | |||
| Design fees @ item £34,000 | |||
| Total construction cost | 825,000 | 275.00 | 100% |























No comments yet